
- #SETUP SNMP TRAP RECEIVER HOW TO#
- #SETUP SNMP TRAP RECEIVER INSTALL#
- #SETUP SNMP TRAP RECEIVER SOFTWARE#
Unknown traps will be logged to /var/log/snmptt/snmpttunknown.log.
Also the file /root/testsuccessful should be created so our custom handler command was also fired.įrom this point on you should be able to create your own handlers. Now you should now have the logfile /var/log/snmptt/snmptt.log created and filled whith your entry. We can give this all a try by entering the following command (best done from another machine to see it´s working from other hosts, change DESTINATIONIP to match yours): snmptrap - v 1 - c public DESTINATIONIP "" "" 1 1 "" To read the traps, Zabbix server or proxy must be configured to start the SNMP trapper process and point to the trap file that. Should show snmpd and snmptrapd are running. To do so edit /etc/snmp/nf and paste the following lines at the end: #ĮVENT test. Now we will create a handler for a test trap. This enables logging all incoming traps to /var/log/snmptt/snmpttunknown.log. Next edit /etc/snmp/snmptt.ini and change unknown_trap_log_enable = 0 This is needed for snmptt to recognize the incoming traps. When a triggering event or condition occurs, the SNMP trap receiver logs the details of the trap message and other information such as the hostname, IP address, and trap type. The ‘-On’ parameter tells snmptrapd to log OID numbers. What does an SNMP trap receiver tool do SNMP trap receiver tools listen for the SNMP trap messages generated by network devices when alert contingencies are met. To TRAPDOPTS = '-On -Lsd -p /var/run/snmptrapd.pid' SNMP trap receiver tools listen for the SNMP trap messages generated by network devices when alert contingencies are met.
#SETUP SNMP TRAP RECEIVER INSTALL#
Installation aptitude install snmp snmpd snmptt ConfigurationĮdit /etc/snmp/nf: # To accept all trapsĪnd change TRAPDOPTS = '-Lsd -p /var/run/snmptrapd.pid' You can also execute a specific command when a trap is received. You can define which incoming traps you want to process and where to log them to (syslog, File, Database).
#SETUP SNMP TRAP RECEIVER HOW TO#
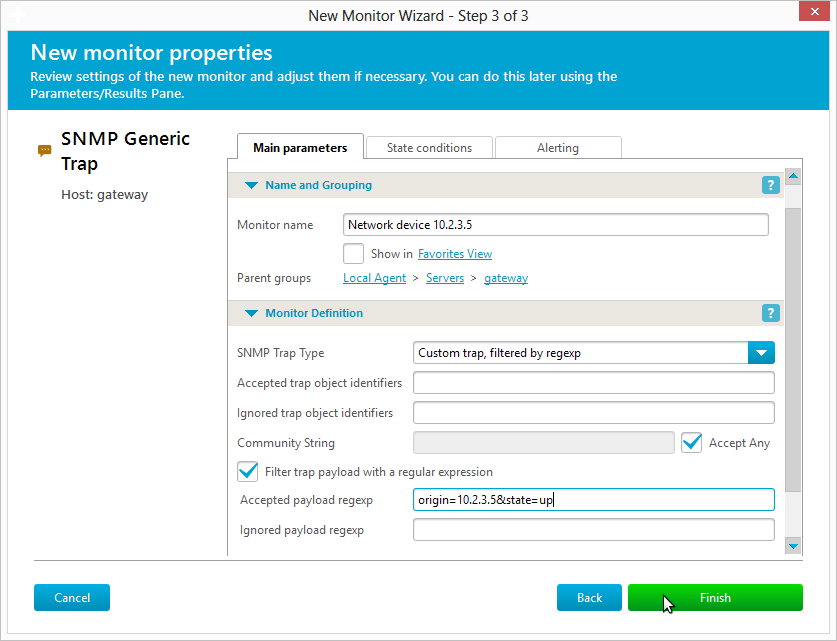
The parameter can be found in General Settings / External / SNMP Traps Integration.The following steps explain how to setup an ubuntu box ( debian should work aswell ) as an snmp trap receiver. But you can enable the "detailed" variant,Īnd all the data received with the trap will be logged. These events can be used for alerting.īy default, only the TrapOID is logged. This will logĪn event of the type trap for received traps. 2504 wl-controller (8.2.151. You can configure generic event logging for snmp traps. So what value should you type in the commands below? Oddly enough, simply supplying no value by using two single quotes '' will instruct the command to obtain the value from the operating system you are executing this on. Sometimes this is the operating system, other devices might use the SNMP engine uptime. Uptime is how long the system has been running since boot. When you send a trap, it must of course conform to a set of standards. If you want to test or store original TRAPS in log then:Ĭreate a folder for storing traps for example in file traps.log Multiple files can be added, separated with. Better is to specify theĮxact MIB files defining the traps you are interested in, for example for LinkDown and LinkUpĪs well as BGP traps, use -m IF-MIB:BGP4-MIB. Will typically fail (snmptrapd cannot load that many mibs).
#SETUP SNMP TRAP RECEIVER SOFTWARE#
Good practice is to avoid -m ALL because then it will try to load all the MIBs in DIRLIST, which Configure SNMP Management Client Software After you have configured a vCenter Server instance or an ESXi host to send traps, configure your management. (For example: /opt/librenms/mibs:/opt/librenms/mibs/cisco:/opt/librenms/mibs/edgecos) Option is not recursive, so you need to specify each DIR individually, separated by. (usually fails)ĭIRLIST: use DIRLIST as the list of locations to look for MIBs. MIBLIST: use MIBLIST ( FILE1-MIB:FILE2-MIB). Use numeric addresses instead of attempting hostname lookups (no DNS) Here is a list of snmptrapd options: Option

In Ubuntu 18 is service located by default in /etc/systemd/system//rvice Description=Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Trap Daemon.ĬonditionPathExists=/etc/snmp/nfĮxecStart=/usr/sbin/snmptrapd -f -m IF-MIB -M /opt/librenms/mibs


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
